Bioretention
Bioretention areas that store and treat runoff are filled with a soil mixture that supports water-tolerant plants. These devices take advantage of natural processes in soils and plants to remove pollutants from stormwater runoff through physical filtration, chemical adsorption, and biological decomposition. The end result is an attractive, landscaped area that cleans and retains stormwater runoff.
For information about bioretention sizing, underdrain design, soil media, construction and maintenance, visit NCSU’s Bioretention website. For information from SC DHEC’s BMP manual, click here.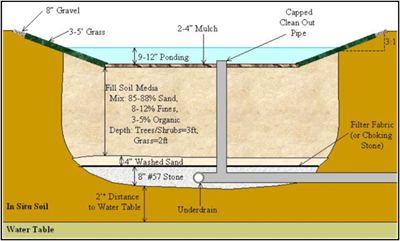
Enhanced Grass Swale
Enhanced grassed swales are gently sloping conveyance channels with a designed underdrain system to filter or infiltrate stormwater runoff as it flows through the channel. Slopes of less than 2 percent are necessary to avoid swale erosion. These are best used along roadways and parking areas in moderate or low density residential or commercial areas.
From Maryland Stormwater Design Manual (2009) Click here for entry in SC DHEC's Stormwater BMP Manual.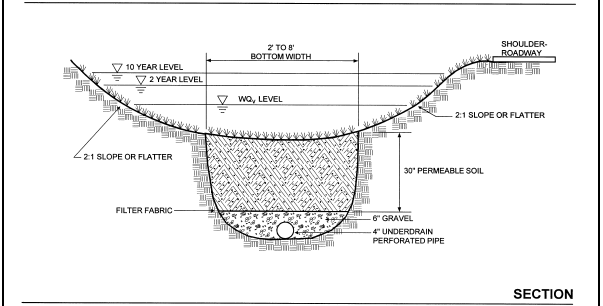
Rooftop Runoff Management
Rooftop runoff management includes the use of cisterns or rain barrels and roof gardens to detain stormwater runoff. Rain barrels and cisterns collect runoff from roofs and store it for household use, such as garden watering. A green roof uses vegetation to soak up and evapotranspire rainfall, much like a bioretention area, before it is discharged. Green roofs require extra engineering to support the weight of the gardens, but can be highly effective in removing pollutants.
From NCDENR Stormwater BMP Manual NCSU Rainwater Harvesting Modeling Tool.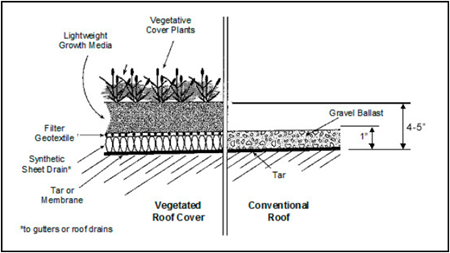
Stormwater Wetlands
Stormwater wetlands are constructed to treat stormwater runoff by mimicking the physical, chemical, and biological functions of natural wetlands. Constructed wetlands consist of shallow pools that support wetland vegetation and wildlife. The natural processes remove pollutants from runoff before discharging to local streams and waterways.
From NCDENR Stormwater BMP Manual For more information about Stormwater Wetlands, visit NCSU’s Stormwater Wetlands website.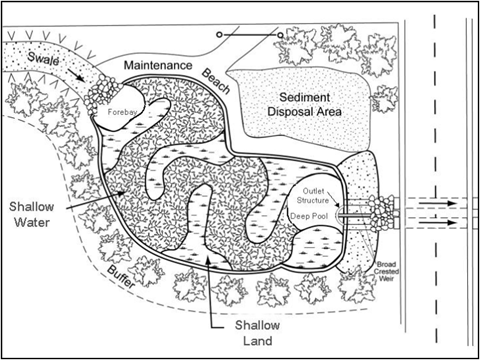
Click here for entry from SC DHEC Stormwater BMP manual.
Infiltration Trench
Infiltration trenches are devices that are designed to fill with stormwater runoff and let it soak into the surrounding soil. These devices allow the water to be filtered and allow biogeochemical processes in the soil to treat the water and remove pollutants. They are most effective for small drainage areas.
From NCDENR Stormwater BMP Manual Click here for entry in SC DHEC's Stormwater BMP Manual.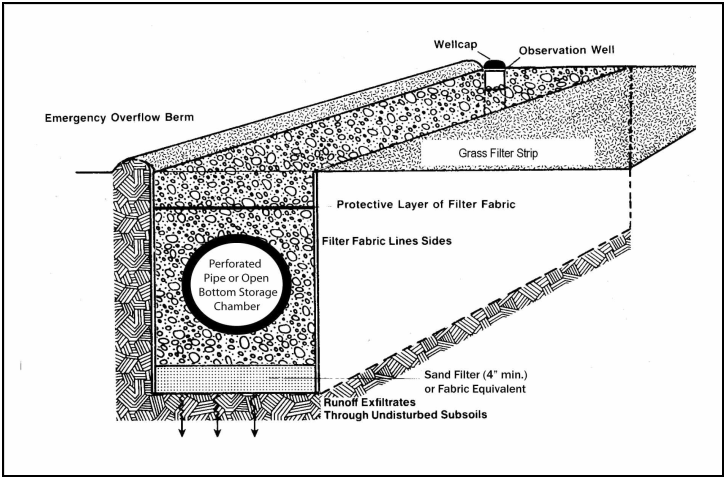
Pervious Pavement
Pervious pavement differs from conventional concrete or asphalt by using air spaces to allow infiltration and storage of stormwater runoff. Conventional pavement generates significant stormwater runoff. Pervious pavement can often reduce the size needed for stormwater detention elsewhere on a developed parcel. Pervious pavement is typically used in low-traffic areas such as parking stalls, emergency lanes, bike paths and sidewalks.
Horry County Pervious Parking Stalls in Garden City Beach Technical Resources Click here for the entry in SC DHEC's Stormwater BMP Manual.
For background and research on pervious pavement, visit NCSU's Biological and Agricultural Engineering pages.
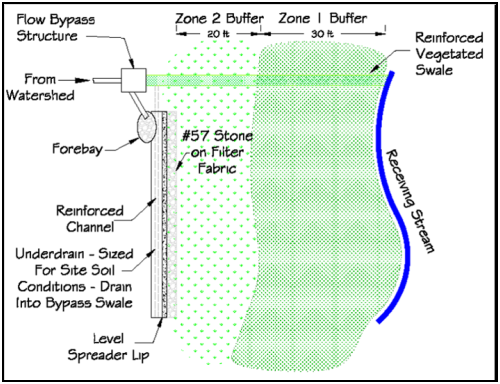
Filter Strip / Level Spreader
Filter strips are vegetated buffers through which diffused stormwater runoff is filtered. The system includes a forebay to dissipate concentrated stormwater runoff, a channel with a level spreader to diffuse the flow, and vegetated buffer or filter strip through which the diffused runoff flows before it enters a waterway or ditch. The buffer is intended to remove sediment and pollutants before it reaches the waterway.
From Low Impact Development: A Guidebook for North Carolina (2009) Click herefor entry in SC DHEC's Stormwater BMP Manual..